Carpenter bees are large, bee-like insects that bore into wood to make their nests They can cause cosmetic and structural damage to untreated wood While sometimes considered pests, carpenter bees are important pollinators. Identifying and understanding the differences between male and female carpenter bees can help guide control efforts.
One key identifier of male carpenter bees is the distinctive yellow dot found on their heads.
Overview of Carpenter Bees
There are two main species of carpenter bees in the United States – the eastern carpenter bee (Xylocopa virginica) and the western carpenter bee (Xylocopa californica) Carpenter bees resemble bumblebees in size and appearance but can be identified by their shiny abdomen lacking dense hair
Carpenter bees have black bodies with yellowish hair concentrated on the thorax. They range from 1/2 to 1 inch long. Only fertilized female bees have the ability to sting, and stings are very uncommon.
Carpenter bees get their name from their nesting habits They bore circular holes into wood, excavating galleries to lay their eggs in. Common nesting sites include untreated lumber, wooden structures, dead trees and posts The holes weaken structures and deform appearances.
Unique Identifiers of Male Carpenter Bees
Male and female carpenter bees can be differentiated by the following characteristics:
-
Size – Male carpenter bees are smaller than females of the same species.
-
Markings – Male carpenter bees have a distinctive yellow dot on the forehead. Females lack the yellow dot and are solid black.
-
Eyes – Male carpenter bees have much larger eyes that almost touch at the top of the head. Female eyes are smaller and widely separated.
-
Legs – Male carpenter bees have more robust, hairy hind legs adapted for mating. Female’s legs are more slender.
-
Stinger – Only female carpenter bees have a stinger. Male’s cannot sting. Their pointy abdomen covers their reproductive parts.
Behavioral Differences
Mating behaviors also differentiate male and female carpenter bees:
-
Territoriality – Male carpenter bees are often seen hovering close by and “inspecting” people near their nests. But they are just curious and guarding territory.
-
Nest Building – Female carpenter bees bore into wood to build egg galleries. Males do not participate in nest construction.
-
Foraging – Only female carpenter bees actively forage for nectar and pollen. Males primarily focus on mating.
-
Mating – Males wait near nests to mate with emerging females. Females mate once to acquire enough sperm to fertilize eggs over their 2-6 week lifespans.
Why Identifying Males Is Important
-
Only female carpenter bees are capable of stinging, so the males present no safety risk. Identifying them prevents needless fear or swatting.
-
Males cannot damage property like females do through nest boring. Leaving them alone prevents harming beneficial pollinators.
-
Males do not need to be directly targeted for control. Keeping females from nesting successfully prevents reproduction and reduces populations over time.
-
Distinguishing males allows using selective control methods. For example, plugging holes after males emerge limits female nesting.
-
Alternatives like wooden bee houses can redirect males away from buildings.
Tips for Identifying and Controlling Carpenter Bees
-
Look for the yellow dot on the head to identify males. Females are solid black.
-
Notice males hovering near nests – they are territorial but harmless.
-
Inspect wood for 1/2 inch round bore holes which indicate carpenter bee nests.
-
Monitor for females chewing new nest entrances, especially in spring.
-
Discourage nesting by painting or sealing exposed wood. Use polyurethane, enamels or varnish.
-
Plug existing holes after males emerge using caulk, wood putty or other sealants. This prevents females from reusing.
-
Apply noisemakers, mint oil or other repellents to deter females from boring new nests.
-
Use insecticidal dust in nest holes to kill young bees and discourage females.
-
Trap males in bee houses placed away from structures to prevent damage.
Identifying the unique yellow dot that distinguishes male carpenter bees can help guide control efforts while supporting these important pollinators. Simple preventive measures and selective management of females provide effective resolution of problems caused by these fascinating insects.
Carpenter Bee Quick Facts
Color: Primarily black with shiny abdomens (not hairy). Males are orange and black, while females are completely black. Number of Legs: SixShape: OvalAntennae: YesRegion: All continents except Antarctica. Carpenter bees can be found all over the United States. The eastern carpenter bee, which is the most common type, can be found as far south as Florida and as far north as Maine.
Types of carpenter bees
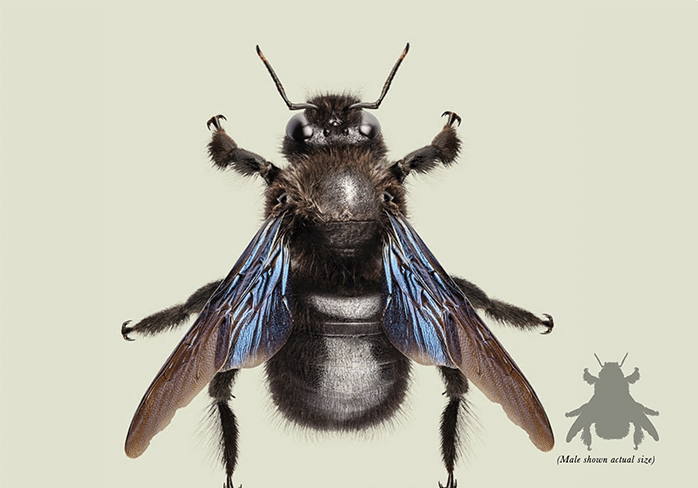
There are hundreds of types of carpenter bee species found all over the world, and each varies in its appearance, location, and overall behavior. For example, the Violet Carpenter Bee is a black bee with dark wings, which in bright light shine purple or blue. This carpenter bee, native to Asia, is active from February to June, raising one and sometimes two broods each year. They nest from April in deadwood, grass stems, or bamboo canes. They also nest in wooden houses and are sometimes regarded as pests (although this bee is not aggressive to humans and rarely stings).
The Eastern Carpenter Bee is a different kind of carpenter bee. It lives in most of the United States and parts of Canada. According to BestBeeBrothers. com, the Eastern Carpenter bee favors structural timbers for nesting, including pine and cedar wood. The Eastern Carpenter Bee is the most common type of carpenter bee. What makes it unique is that it can cut into the sides of flower petals to get to the nectar without pollinating them. This is how it got the name “nectar robber.” People often notice that this species of bee has jawbones that help it collect nectar better than other types of carpenter bees.
The largest bee in California is the California Carpenter Bee, which is also called the Valley Carpenter Bee. It is from western North America. This carpenter bee makes its nest by creating long, double-ended passages in the limbs of oak trees. OurCityForest. org, their nests are usually watched over and cared for by a mother bee and her unmarried daughters. The male Valley Carpenter Bee is very rarely seen.
Do Carpenter Bees Sting?
FAQ
Do yellow head bumble bees sting?
Do carpenter bumble bees sting?
Are Valley carpenter bees poisonous?
Do whitehead bumble bees sting?
What does a carpenter bee look like?
These large bees have a black and hairless abdominal region. The males can sometimes have patches of short hair on the abdomen and a yellow or white face. They may also have a white dot on their heads. Female carpenter bees, however, have black faces. They’re approximately 1/2 inch to 1 inch long and sometimes mistaken for bumblebees.
How do you know if a bumblebee is a carpenter bee?
While a bumblebee’s will be covered in small hairs, carpenter bee abdomens are hairless. Carpenter bee abdomens are black, but a bumblebee’s abdomen will usually have yellow markings. Rule out carpenter bees if you see external nests. If you see a traditional-looking bee nest hanging from a tree, you are likely dealing with bumblebees.
How big do carpenter bees get?
Carpenter bee sizes vary, and they can be anywhere between a half and one inch long. Carpenter bees don’t live in colonies though, and the differences between male and female bees are superficial. Females have black heads, and males have white markings on their faces. Other than that, they’re almost exactly the same—even in size.
How do you spot a carpenter bee?
Other pro tips to help you spot carpenter bees include: Look for circular holes in wood: As mentioned, carpenter bees excavate circular holes in wood to create their nests. These holes are often visible on wooden structures. Search for piles of sawdust: Carpenter bees leave sawdust piles while making these holes.
Do eastern carpenter bees have marking chemicals?
Eastern carpenter bees have mandibular glands that are known to produce a marking chemical in X. hirsutissima that functions as a nest marker or for female attraction. The glands are present in both males and females, but they produce no marking substance. [ 2 ]
What does a carpenter bee sound like?
Carpenter bees also have a distinctive “buzzing” sound when they fly. Carpenter bees are active during the day, especially in the spring and summer. They’re attracted to flowers, where they collect pollen and nectar to feed their young. Additionally, carpenter bees prefer to nest in soft, dead wood.
